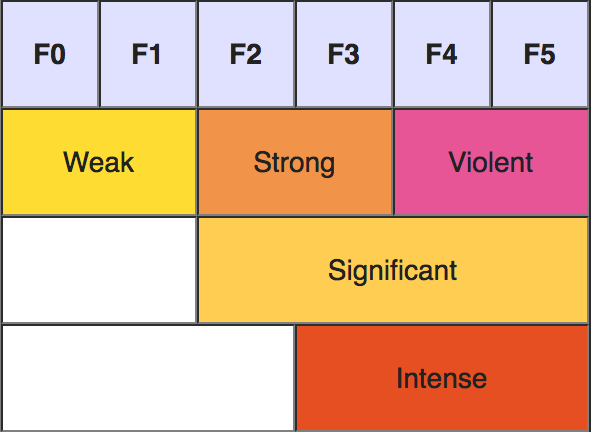
Tornado Scale
Tornadoes are rated by their intensity and the damaged they cause to vegetation and human created structures. The Fujita scale (F-Scale), also known as the Fujita-Pearson scale, is a tornado scale that was introduced in 1971 by Tetsuya Fujita. In the United States the Fujita scale was replaced with the Enhanced Fujita scale (EF-Scale), which is now the primary scale used the United Sites and Canada. The original Fujita scale was decommissioned in 2007.
Choose a Tornado Scale
- The Fujita Tornado Scale - this tornado scale was used between 1971 to 2007...
- The Enhanced Fujita Tornado Scale - This is the tornado scale currently in use...
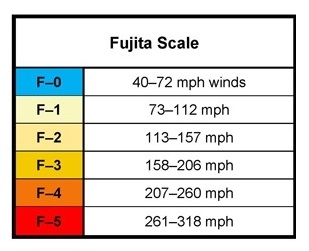
The Fujita Tornado Scale
The Fujita tornado scale was created by Tetsuya Fujita and in 1971 in collaboration with Allen Pearson. This method is a sliding scale 0 to 5 with 5 being the most violent. For example, the Tri-State Tornado was an F5 tornado, which was one of the most violent and deadliest tornadoes in history. Below is a brief description of each type of tornado on the Fujita scale.
- Wind speeds between 40 to 72 mph (64 to 116 km/h)
- Light damage
- Broken branches; shallow rooted trees pushed over; some chimney damage.
- Wind speeds between 73 to 112 mph (117 to 180 km/h)
- Moderate damage
- Surface damage to roofs; mobile homes pushed off foundation; moving vehicles pushed off the road.
- Wind speeds 113 to 157 mph (181 to 253 km/h)
- Significant damage
- Frame houses have roof torn off; mobile homes complete destroyed; train boxcars overturned; large trees snapped or uprooted; smaller debris turned into missiles.
- Wind speeds between 158 to 206 mph (254 to 332 km/h)
- Severe damage
- Roofs completely torn off well-constructed buildings, along with some walls, majority of trees uprooted, trains overturned, vehicles lifted off the ground.
- Wind speeds between 207 to 260 mph (333 to 418 km/h)
- Devastating damage.
- Well-constructed houses are completely destroyed; structures with weak foundations blown away; vehicles could be thrown; large debris become flying missiles.
- Wind speeds between 261 to 318 mph (419 to 512 km/h)
- Incredible damage
- Most structures severely damaged or completely destroyed, vehicles can become flying missiles.
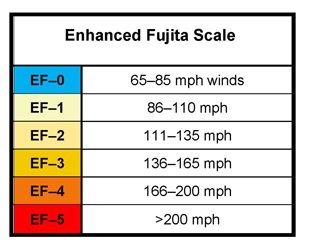
The Enhanced Fujita Tornado Scale
The enhanced Fujita tornado scale was created by Fujita Scale Enhancement Project between 2000 and 2004. The enhanced Fujita scale still uses the same basic principles as the original Fujita scale. There are six categories of tornadoes, 0 to 5. Wind speeds were revised and it also adds more type of structures and vegetation, expands degrees of damage, and better accounts for variables such as differences in construction quality. Below is a brief description of each type of tornado on the Fujita scale.
EF0 Tornado
- Wind speeds between 65 to 85 mph (104 to 137 km/h)
- Light damage
- Broken branches; shallow rooted trees pushed over; some chimney damage.
EF1 Tornado
- Wind speeds between 86 to 110 mph (138 to 177 km/h)
- Moderate damage
- Surface damage to roofs; mobile homes pushed off foundation; moving vehicles pushed off the road.
EF2 Tornado
- Wind speeds between 111 to 135 mph (178 to 217 km/h)
- Significant damage
- Frame houses have roof torn off; mobile homes complete destroyed; train boxcars overturned; large trees snapped or uprooted; smaller debris turned into missiles.
EF3 Tornado
- Wind speeds between 136 to 165 mph (218 to 266 km/h)
- Severe damage
- Roofs completely torn off well-constructed buildings, along with some walls, majority of trees uprooted, trains overturned, vehicles lifted off the ground.
EF4 Tornado
- Wind speeds between 166 to 200 mph (267 to 322 km/h)
- Devastating damage.
- Well-constructed houses are completely destroyed; structures with weak foundations blown away; vehicles could be throne; large debris become flying missiles.
EF5 Tornado
- Wind speeds greater than 200 mph (322+ km/h)
- Incredible damage
- Most structures severely damaged or completely destroyed, vehicles can become flying missiles.
In addition to classification by wind speed there are also 28 damage indicators (DI), or types of structures and vegetation, each with a varying number of degrees of damage (DoD).
| DI No. | DI Abbv. | Damage Indicator (DI) | Degrees of Damage (DoD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SBO | Small barns, farm outbuildings | 8 |
| 2 | FR12 | One- or two-family residences | 10 |
| 3 | MHSW | Single-wide mobile home (MHSW) | 9 |
| 4 | MHDW | Double-wide mobile home | 12 |
| 5 | ACT | Apt, condo, townhouse (3 stories or less) | 6 |
| 6 | M | Motel | 10 |
| 7 | MAM | Masonry apt. or motel | 7 |
| 8 | SRB | Small retail bldg. (fast food) | 8 |
| 9 | SPB | Small professional (doctor office, branch bank) | 9 |
| 10 | SM | Strip mall | 9 |
| 11 | LSM | Large shopping mall | 9 |
| 12 | LIRB | Large, isolated ("big box"") retail bldg." | 7 |
| 13 | ASR | Automobile showroom | 8 |
| 14 | ASB | Automotive service building | 8 |
| 15 | ES | School - 1-story elementary (interior or exterior halls) | 10 |
| 16 | JHSH | School - jr. or sr. high school | 11 |
| 17 | LRB | Low-rise (1-4 story) bldg. | 7 |
| 18 | MRB | Mid-rise (5-20 story) bldg. | 10 |
| 19 | HRB | High-rise (over 20 stories) | 10 |
| 20 | IB | Institutional bldg. (hospital, govt. or university) | 11 |
| 21 | MBS | Metal building system | 8 |
| 22 | SSC | Service station canopy | 6 |
| 23 | WHB | Warehouse (tilt-up walls or heavy timber) | 7 |
| 24 | TLT | Transmission line tower | 6 |
| 25 | FST | Free-standing tower | 3 |
| 26 | FSP | Free standing pole (light, flag, luminary) | 3 |
| 27 | TH | Tree - hardwood | 5 |
| 28 | TS | Tree - softwood | 5 |